Pancreatitis Treatment in Vizag
Introduction
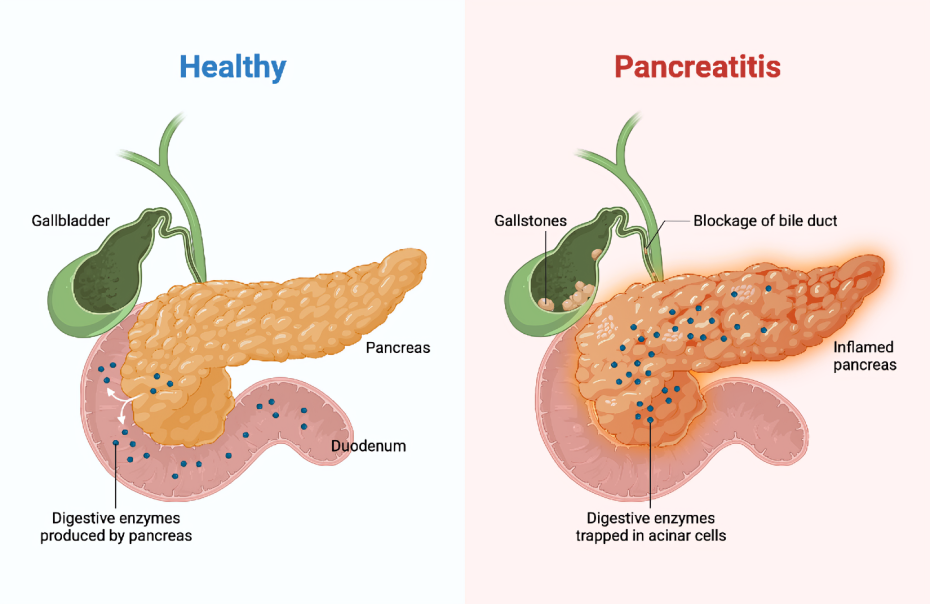
Pancreatitis is a medical condition characterized by inflammation of the pancreas, an essential organ responsible for producing digestive enzymes and hormones like insulin. It can occur as either acute pancreatitis (develops suddenly and lasts for a short period) or chronic pancreatitis (persists over time and may lead to permanent damage). Both forms can range from mild symptoms to severe complications, making early diagnosis and treatment crucial.
Types of Pancreatitis
Acute Pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis typically begins with sudden pain in the upper abdomen that may radiate to the back. The pain can vary from mild to severe and may last for several days. Common symptoms include nausea, vomiting, fever, and abdominal tenderness. Severe cases can lead to complications such as infection, organ failure, or jaundice caused by bile duct obstruction.
Chronic Pancreatitis
Chronic pancreatitis is a long-term condition where repeated inflammation leads to scarring and loss of pancreatic function. Symptoms often include persistent abdominal pain that worsens after eating, weight loss due to malabsorption of nutrients, and the development of diabetes in advanced stages. Unlike acute pancreatitis, chronic cases may remain asymptomatic until complications arise.
Causes of Pancreatitis
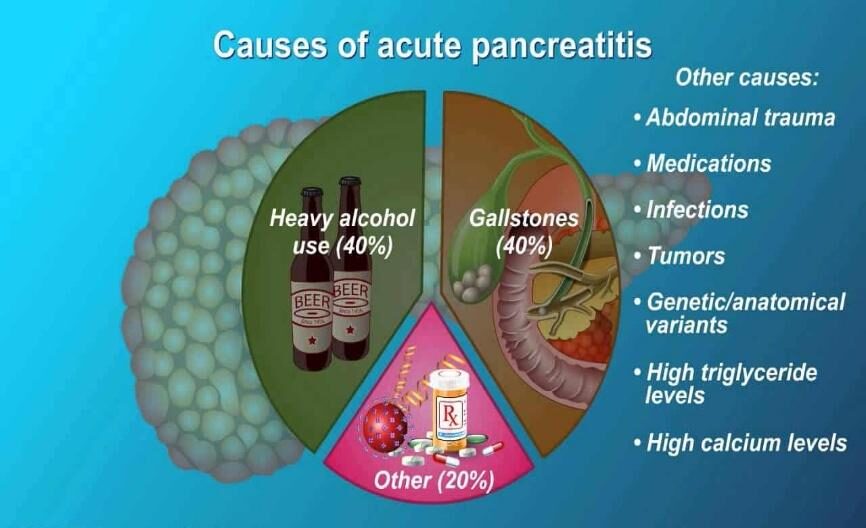
The primary causes of pancreatitis include:
- Alcohol Abuse: Heavy alcohol consumption can lead to pancreatitis.
- Gallstones: Gall bladder stone slips down and block the opening of pancreatic duct, leading to release of enzymes within the gland and causing inflammation.
- Genetic Factors: Certain hereditary conditions increase susceptibility.
- Medications: Some drugs like steroids, opioids etc can trigger pancreatic inflammation.
- Other Causes: High blood calcium or lipid levels, injury to abdomen, infections, and medical procedures like ERCP.
In many cases of chronic pancreatitis, the exact cause remains unknown (idiopathic pancreatitis).
Diagnosis
Diagnosing pancreatitis involves a combination of detailed medical history analysis, physical examinations, and diagnostic tests:
- Lab Tests: Blood tests measure elevated levels of pancreatic enzymes (amylase and lipase), raised lipids, and signs of infection or inflammation.
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasound detects gallstones; CT scans and MRCP provide detailed images of the pancreas and ducts.
- Stool Tests: Used in chronic cases to check for fat malabsorption.
Early diagnosis is vital to prevent complications such as necrosis (dead tissue within gland) or haemorrhage (bleeding).
Treatment
Acute Pancreatitis
Main stay of treatment for acute pancreatitis focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications like sepsis, infection/ abscess (pus), pseudocyst (fluid filled sac near pancreas):
- Hospitalization: Patients often require IV fluids for hydration, pain management is crucial along with requirement of antibiotics (few cases), and nutritional support through feeding tubes if necessary.
- Surgery: In cases caused by gallstones or duct obstructions, surgical intervention (ERCP – endoscopic procedure) may be needed. If patient is in sepsis and suspecting any necrosis in pancreas (dead tissue or infected material), may need immediate surgical intervention (necrosectomy) if not responding to antibiotics.
Chronic Pancreatitis
Management of chronic pancreatitis aims to reduce recurrence and severity of symptoms and prevent further damage:
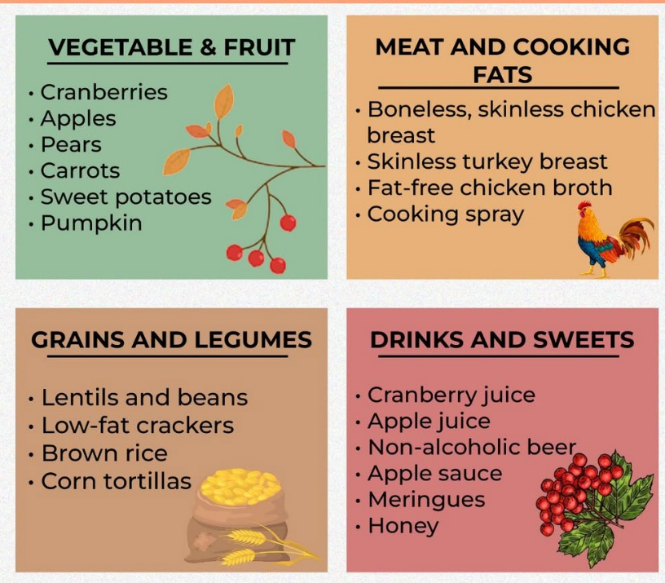
- Dietary Changes: A low-fat diet with high protein and carbohydrates is recommended. Smaller meals help reduce strain on the pancreas.
- Medications: Pancreatic enzyme supplements aid digestion.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Avoiding alcohol and quitting smoking are critical steps in managing chronic pancreatitis.
- Surgical intervention: To remove damaged part of pancreas and divert the pancreatic juices into intestine (connecting pancreatic duct to intestine).
Prevention
- Gallstone Prevention: Maintain a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-cholesterol foods. Even if diagnosed, timely treatment should be done.
- Alcohol Moderation: Limit alcohol intake or avoid it entirely if you have had alcohol-related pancreatitis.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Quit smoking and manage conditions like high cholesterol or obesity that increase risk factors for pancreatitis.
Post-Treatment Care
- Follow a low-fat diet with clear liquids initially after acute episodes.
- Gradually reintroduce solid foods under medical supervision.
- Take prescribed pancreatic enzyme supplements (usually in chronic patients) with meals to improve nutrient absorption.
- Monitor for complications such as diabetes or recurrent episodes.
- Regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider are essential for long-term management.
Conclusion
Pancreatitis is a serious condition that requires prompt attention to avoid life-threatening complications. With advancements in diagnostic tools and treatment options, patients can achieve better outcomes when supported by proper medical care and lifestyle modifications. Don’t hesitate to consult our expert professionals at “Vizag Surgicare” if you have any abdominal symptoms or need to clarify any doubts.
Need Help?
We’re Just a Call Away!
Pancreatic Pseudocyst
Introduction
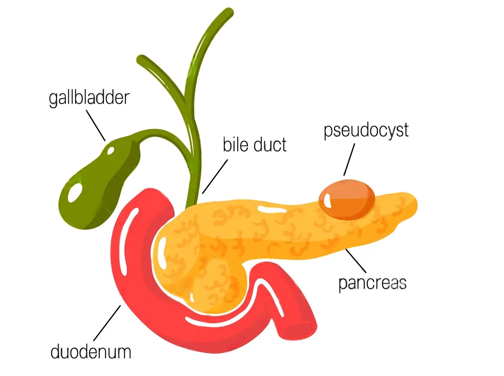
A pancreatic pseudocyst is a fluid-filled sac (without epithelial lining) that forms in the pancreas, often as a complication of pancreatitis (acute or chronic) and sometimes from injury to abdomen.
Symptoms
Symptoms can appear immediately after pancreatitis or months later.
- Abdominal pain lasting > 4 weeks
- Bloating/ indigestion
- Nausea/ vomiting
- Early satiety
Diagnosis
Diagnosis includes detailed history and physical examination. Confirmation is done by imaging – Ultrasound abdomen/ CT. CT provides much more details than ultrasonography like location, size, communication with adjacent ducts, content of the sac (clear fluid or infective/ thick material).
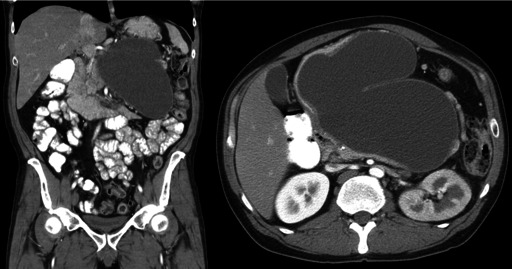
Complications and Treatment:
Complications from pancreatic pseudocysts can be severe and include infection leading to sepsis, hemorrhage, obstruction of nearby structures (compression), and rupture.
Treatment often involves drainage of the pseudocyst, which can be done through endoscopic, percutaneous, or surgical methods. Minimally invasive techniques are preferred for their faster recovery times and lower risk of complications.
In some cases, small pseudocysts may resolve on their own without treatment, but larger ones or those causing symptoms or suspicion of malignancy (cancer) typically require intervention. The “Rule of 6” suggests that treatment may be necessary if a pseudocyst is larger than 6 cm or has been present for more than 6 weeks.
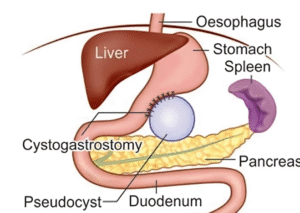
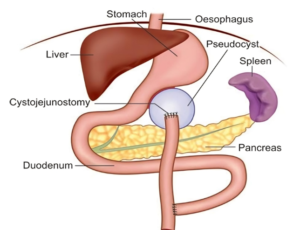
Conclusion
Pancreatic pseudocysts are a significant concern for individuals with pancreatitis, requiring careful monitoring and sometimes urgent medical intervention. Advances in medical technology have made treatment more efficient and safer. Consult our professionals at “Vizag Surgicare” for expert care and treatment.
contact us
Get In Touch With Us
phone number
Mobile No 1 : +91-77029 50513
Mobile No 2 : +91-9848638615
Mobile No 3 : +91-9849239213
our address
First Floor, Mohan Medical Shop, Seethammadhara (NE), Visakhapatnam-530013
email address
info@vizagsurgicare.com
