Peptic ulcer perforation
Introduction
Peptic ulcer perforation is a serious life-threatening complication of peptic ulcer disease (PUD). It occurs when an ulcer creates a hole in the wall of the stomach or duodenum (small intestine), allowing digestive contents to leak into the abdominal cavity. This condition requires emergency medical attention due to the risk of peritonitis and sepsis.
Causes / Risk factors
The primary causes of peptic ulcer perforation are:
- Helicobacter pylori infection: Most common cause of PUD. This bacterium damages the mucosal lining and makes it susceptible for the damage to increased acid secretion. It is common in low socio-economic group and is transmitted through faeco-oral route (through contaminated faeces or stool or poop).
- NSAID (Pain killers) abuse: Chronic use of medications like aspirin or ibuprofen increases the risk of ulcers and their complications like perforation.
- Lifestyle factors: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption contribute to ulcer formation and delayed healing.
- Other medical conditions: Chronic illnesses like liver or kidney disease, hyperparathyroidism, and stress can also increase susceptibility.
Symptoms of a Perforated Ulcer
Often very severe-
- Sudden, sharp abdominal pain (remember exact time due to its intensity)
- Nausea and vomiting
- Rigid, board-like abdomen with absent bowel sounds
- Fever and chills
- Rapid heart rate, low blood pressure and other features of sepsis.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosing peptic ulcer perforation involves a combination of clinical evaluation and imaging studies:
- Clinical examination: Includes detailed medical history and examination of abdomen for tenderness, rigidity and signs of peritonitis.
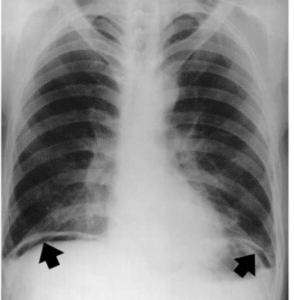
Imaging: X-ray erect abdomen with lower lobes may show free air under the diaphragm (pneumoperitoneum), while a CT scan provides more detailed information about the location of perforation and can comment on surrounding structures.

Treatment
Treatment options for peptic ulcer perforation involves both surgical and medical management depending on severity of the condition.
Medical or Non-surgical Management:
It is reserved only for selected patients who are stable and the perforation is concealed without generalised peritonitis. This includes –
- Decompression of stomach by Nasogastric tube aspiration
- Keeping patient nil by mouth (NBM) and giving rest to gastrointestinal tract
- Broad spectrum antibiotics to prevent infection
- Maintaining hydration and nutrition supplementation with IV fluids and Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN).
- Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) to reduce gastric acid secretion and should be used for longer duration than usual.
It has high chances of complications like intraabdominal abscess and delayed healing of perforation.
Surgical Treatment:
Surgery remains the gold standard treatment in managing cases of peptic ulcer perforation.
- Ideally Emergency midline laparotomy is done. However, Laparoscopic approach can be tried in some stable patients. All infected fluid is sucked out. Perforation (hole) is identified and closed with piece of omentum (fatty tissue that supports and covers the intestine).

Post-Treatment Care
Recovery from peptic ulcer perforation requires careful post-treatment care to manage underlying causes and prevent recurrence:
- Eradication of H. pylori infection: Patients diagnosed with H. pylori infection are treated with a combination of antibiotics and PPIs.
- Lifestyle modifications: Quitting smoking, reducing alcohol intake, and avoiding NSAIDs (pain killers) are crucial steps in preventing future ulcers.
- Regular follow-ups: Patients should undergo periodic endoscopic evaluations to monitor healing and rule out malignancy (cancer) in peptic ulcers.
- Nutritional support: A gradual return to normal diet under medical supervision ensures proper recovery. Eat small and frequent meals.
Conclusion
Peptic ulcer perforation is a medical emergency that requires early diagnosis, emergency surgery and skilled care for full recovery. Stay alert to symptoms, manage risk factors, and seek help early to prevent this dangerous complication.
If you are experiencing symptoms of a perforated ulcer or chronic abdominal pain, consult our healthcare professionals at “Vizag Surgicare”. Early treatment saves lives.
contact us
Get In Touch With Us
phone number
Mobile No 1 : +91-77029 50513
Mobile No 2 : +91-9848638615
Mobile No 3 : +91-9849239213
our address
First Floor, Mohan Medical Shop, Seethammadhara (NE), Visakhapatnam-530013
email address
info@vizagsurgicare.com
