Scrotal Conditions Treatment in Vizag
Introduction
The scrotum is a vital part of the male reproductive system – a pouch of skin located below the penis that contains and protects the testicles. It plays a key role in regulating the temperature of the testes, which is essential for healthy sperm production.
Several conditions can affect the scrotum, ranging from mild discomfort to serious issues that may impact fertility or require surgical intervention. Some of the most common scrotal conditions include :
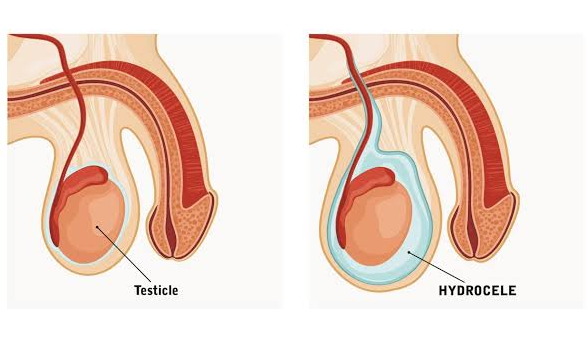
- Hydrocele – A fluid buildup around the testicle causing painless swelling.
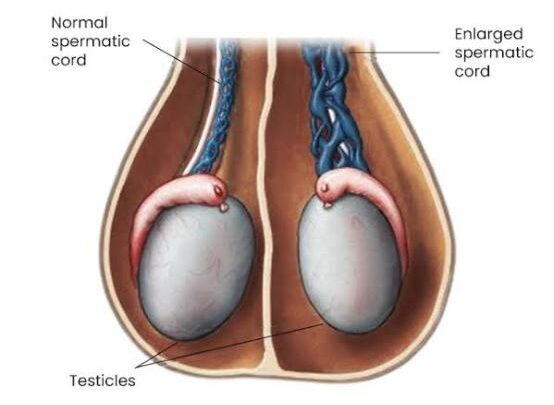
- Varicocele – Enlarged veins in the scrotum that can lead to pain and infertility.
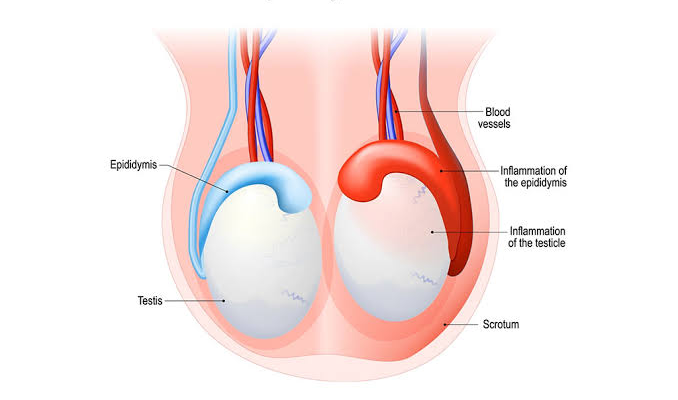
- Epididymitis – Inflammation of the epididymis, often caused by infection.
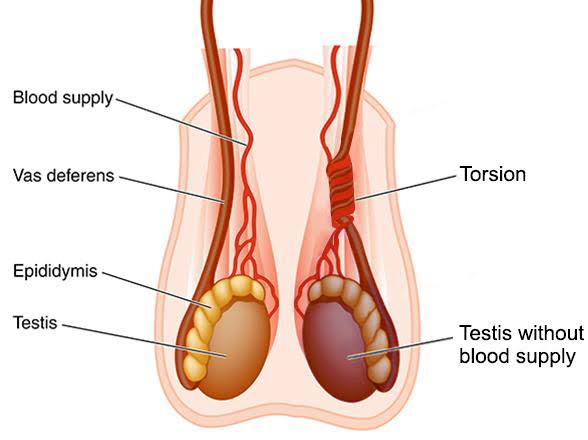
- Testicular torsion – A medical emergency where the spermatic cord twists, cutting off blood supply.
1. Hydrocele
Introduction
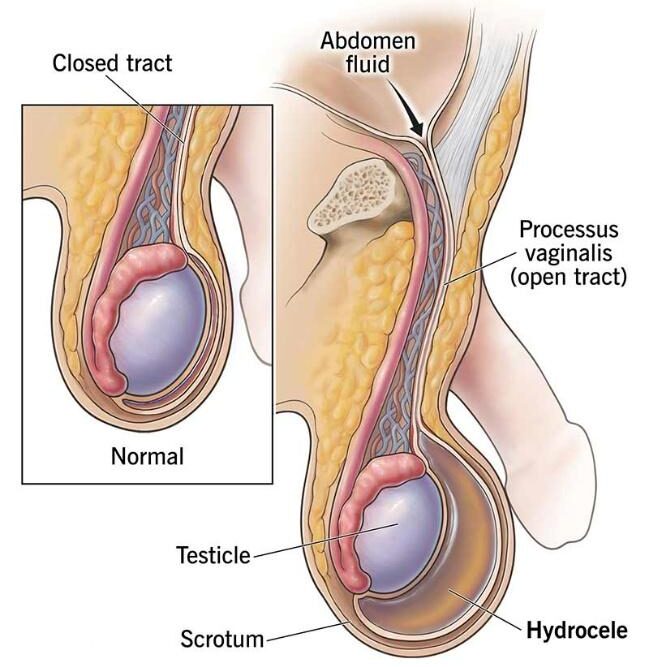
A hydrocele is a fluid-filled sac surrounding a testicle, leading to painless swelling of the scrotum. It can occur at any age but is more common in newborns and older men.
Causes
- In infants who have hydrocele from birth (congenital hydrocele), there is flow of abdominal fluid into the scrotum due to failure of closure of processus vaginalis at birth. And sometimes, even if the processus vaginalis closes on its own, abdominal fluid may remain in the scrotum but child’s body usually absorbs this fluid within first two years.
- In adults (acquired hydrocele), it may result from injury/ inflammation/ infection/ blockage of lymphatics/ cause is unknown (idiopathic).
Symptoms
- A swollen or enlarged scrotum
- A feeling of heaviness or discomfort
- Usually painless, unless very large or infected
Treatment:
Treatment depends on the severity and cause.
- Non-surgical management involves observation, especially if the hydrocele is small, painless, and not causing discomfort.
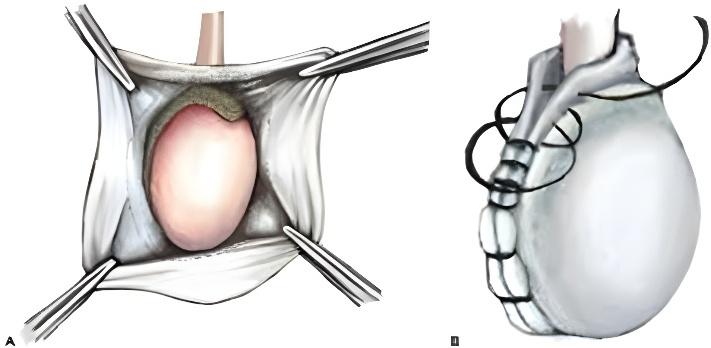
- Surgical treatment, known as hydrocelectomy, is recommended when the swelling becomes large or painful. The procedure involves removing the fluid-filled sac through a small incision and is typically performed on an outpatient basis with a high success rate and minimal complications.
Recovery:
- Post operative recovery includes management of pain with pain killers.
- Scrotal wall swelling is normal and is relieved within 7-10 days with good scrotal support
- Maintain hygiene to prevent surgical site infection.
- Can get back to routine activity once the patient is comfortable.
Need Help?
We’re Just a Call Away!
2. Varicocele
Introduction
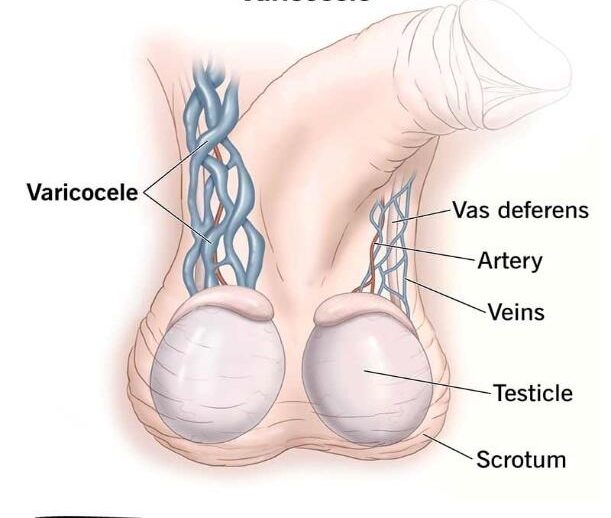
A varicocele is an enlargement of the veins within the scrotum, similar to varicose veins in the legs. It is more common on the left side than right, due to anatomical differences in venous drainage. The exact cause is unknown. Varicoceles are a leading cause of male infertility and can develop during puberty or later in life.
Symptoms
Usually asymptomatic in majority of individuals. However, it may present as
- Dull aching in scrotal region, which often gets better on lying down.
- Swelling in testicles or scrotum
- Infertility
Diagnosis
- Physical examination revealing “Bag of worms” feel
- Scrotal colour doppler measures the diameter of the dilated veins
- Semen analysis to know the impact of varicocele on fertility
Treatment
Treatment options vary based on complaints and severity (grade of varicocele)
Non-surgical approaches include lifestyle changes –
- Avoiding prolonged standing or heavy lifting
- Wearing supportive underwear
- Managing discomfort with pain relievers
Surgical options involve
- Varicocelectomy (surgically ties off the affected veins) – can be done in open technique or by laparoscopic approach
- Embolization, a minimally invasive procedure where coils or agents are used to block the faulty veins.
Both methods aim to restore proper blood flow by relieving pooling of venous blood and improve fertility.
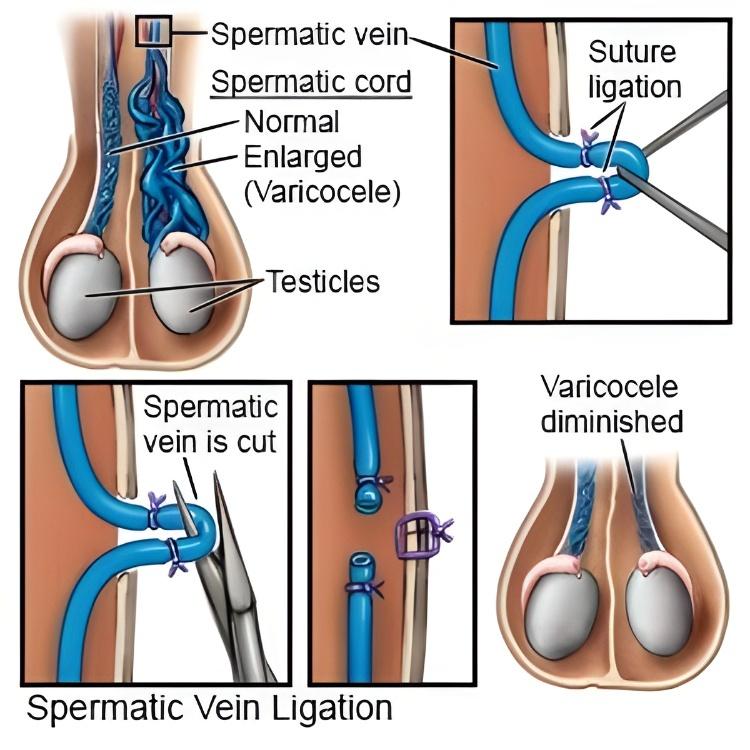
Recovery
- Post procedural pain is manageable with pain killers.
- Good scrotal support to reduce discomfort and swelling
- Routine light work can be regained within 2-3 days
- Avoid strenuous activity or lifting heavy weights for 3-4 weeks
- Maintain good hygiene to prevent infections
- Sexual activity can be regained after 6-8 weeks
- Supportive medications helping in enhancing sperm production in patients with infertility.

3. Testicular Torsion
Introduction
Testicular torsion is a condition where the spermatic cord, which supplies blood to the testicle, twists and cuts off blood flow. This causes sudden and severe pain and swelling in one testicle. It usually affects young boys between 12-18 years but can happen at any age. Sometimes linked to injury or sudden movement, but it can also occur during sleep. It is a medical emergency that needs immediate treatment to save the testicle.
Causes
Many people with testicular torsion have a condition called the “bell clapper deformity“, where the testicle is not properly attached inside the scrotum and can twist freely. This twisting blocks blood flow and causes pain.
Symptoms
- Sudden, severe pain in one testicle or scrotum
- Swelling and redness of the scrotum
- Testicle positioned higher or at an unusual angle
- Pain that may spread to the lower abdomen or thigh
- Nausea and vomiting
- Difficulty walking due to pain
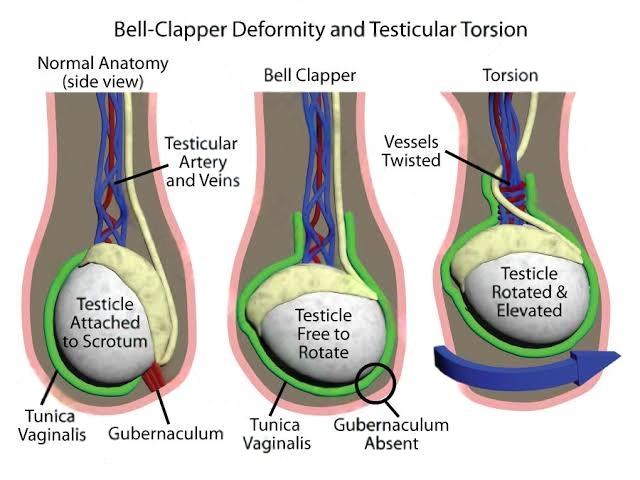
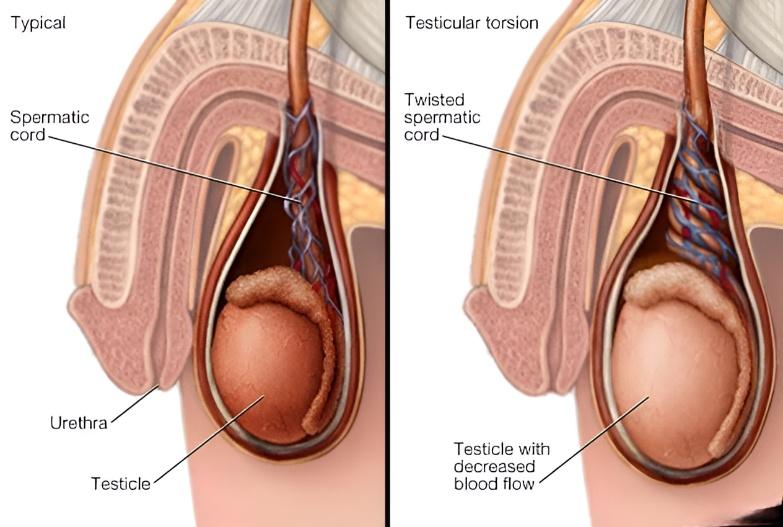
Management
Treatment of testicular torsion is utmost emergency, as delay can lead to permanent damage of the testis. Surgery within 6 hours of pain onset gives the best chance to save the testicle.
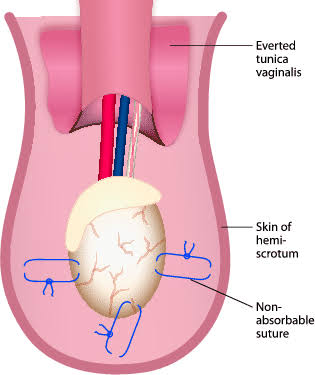
- Surgical detorsion and orchiopexy : This technique involves de-rotation of the testis and fixation to the scrotum (3-point fixation) to prevent rotation again.
- Always opposite side testis is also fixed
- In cases with delayed presentation, and loss of viability of testis (dead testicular tissue) orchidectomy (removal of testis) should be performed to prevent anti-sperm antibodies and further damage of the opposite side testis.
Post Surgery Care
- Good scrotal support to reduce swelling
- Avoid strenuous exercise or running for 6-8 weeks
- Avoid injury to scrotum
If you or your child has sudden testicular pain or swelling, go to the hospital immediately. Do not wait—every minute counts.
Conclusion
If you experience scrotal swelling or discomfort, consult “Vizag Surgicare” for expert evaluation and effective treatment options as per the condition.
contact us
Get In Touch With Us
phone number
Mobile No 1 : +91-77029 50513
Mobile No 2 : +91-9848638615
Mobile No 3 : +91-9849239213
our address
First Floor, Mohan Medical Shop, Seethammadhara (NE), Visakhapatnam-530013
email address
info@vizagsurgicare.com
