Vascular conditions Treatment in Vizag
Introduction
Vascular conditions comprise a wide range of diseases that affect the body’s blood vessels, including arteries, veins, and lymphatic vessels. These vessels are responsible for transporting oxygen, nutrients and waste products throughout the body. When these vessels become diseased or damaged-due to factors like plaque buildup (atherosclerosis), inflammation, or valve dysfunction-blood flow can be impaired, leading to symptoms such as pain, swelling, skin ulcers, and increased risk of blood clots. Most common vascular diseases that we encounter routinely include peripheral artery disease (PAD) and varicose veins. Early diagnosis and appropriate management, including lifestyle changes, medication or surgery, are essential to prevent serious complications and maintain overall vascular health.
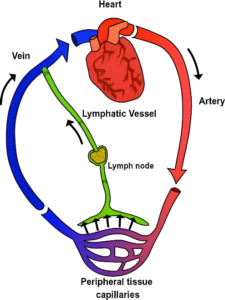
1. Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)
Introduction
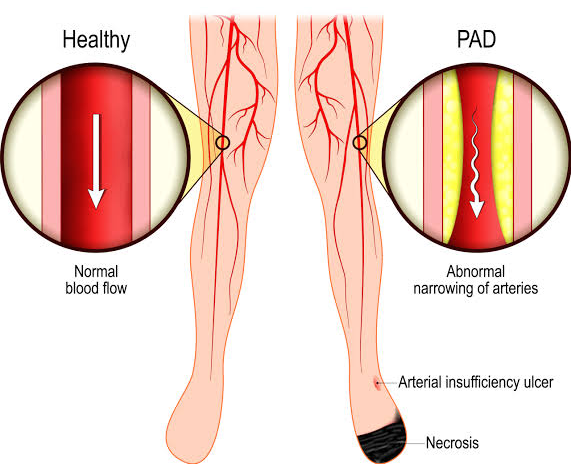
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD) is a common condition where the arteries that carry blood to your legs or arms become narrow or blocked, reducing blood flow. It happens when fatty deposits called plaque build-up inside the arteries, a process known as atherosclerosis or because of blockage of flow due to clot formation known as thrombosis and can cause symptoms like leg pain when walking.
Causes of PAD :
- Atherosclerosis: Most common cause, where cholesterol plaque narrows arteries.
- Blood clots : Can suddenly block arteries – acute emergency
- Inflammation : Tightens and hardens arteries secondary to fibrosis and thereby reducing the lumen of the vessel.
- Injury or radiation : Damage to arteries can reduce blood flow secondary to radiation induced fibrosis.
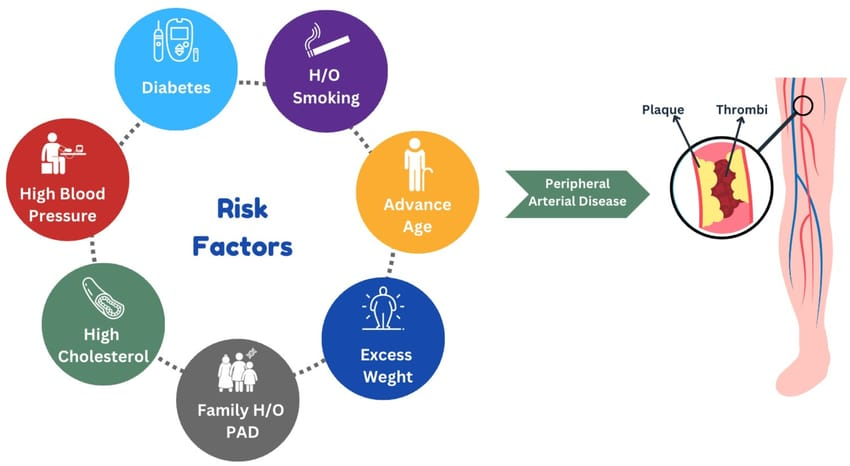
Risk Factors
- Smoking (most significant risk)
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure and cholesterol
- Older age
- Obesity
- Lack of physical activity
- Family history of heart disease
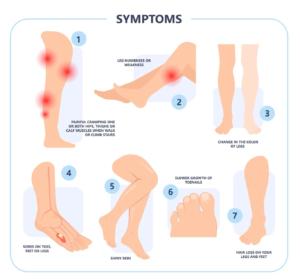
Symptoms:
- Cramping, aching, or pain in leg muscles during walking or climbing stairs (claudication pain)
- Numbness or weakness in legs
- Coldness or colour changes in feet or legs
- Slow-healing sores or ulcers on legs or feet
- Hair loss or decreased toenail growth on legs
- Shiny skin
Not everyone has symptoms — sometimes PAD is silent but still dangerous.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis includes thorough clinical assessment of peripheral pulses along with detailed history and series of investigations like –
- Colour Doppler to check blood flow
- CT or MR Angiogram to know the detailed status of arteries and about collaterals (blood flow from the surroundings)
Treatment Options
Lifestyle Changes
- Quit smoking
- Healthy diet – low in saturated fats
- Regular exercise, especially walking programs to improve leg circulation
- Control diabetes, blood pressure, and cholesterol
Medications
- Statins to lower cholesterol and reduce plaque buildup
- Blood pressure medicines – controls BP and prevent damage of vessels due to high blood pressure
- Antidiabetic medications – strict control of sugar levels
- Antiplatelet drugs like Aspirin to prevent clots and in high-risk patients Clopidogrel is also added
- Medicines like Cilostazole to improve blood flow and reduce leg pain
Surgical Treatments
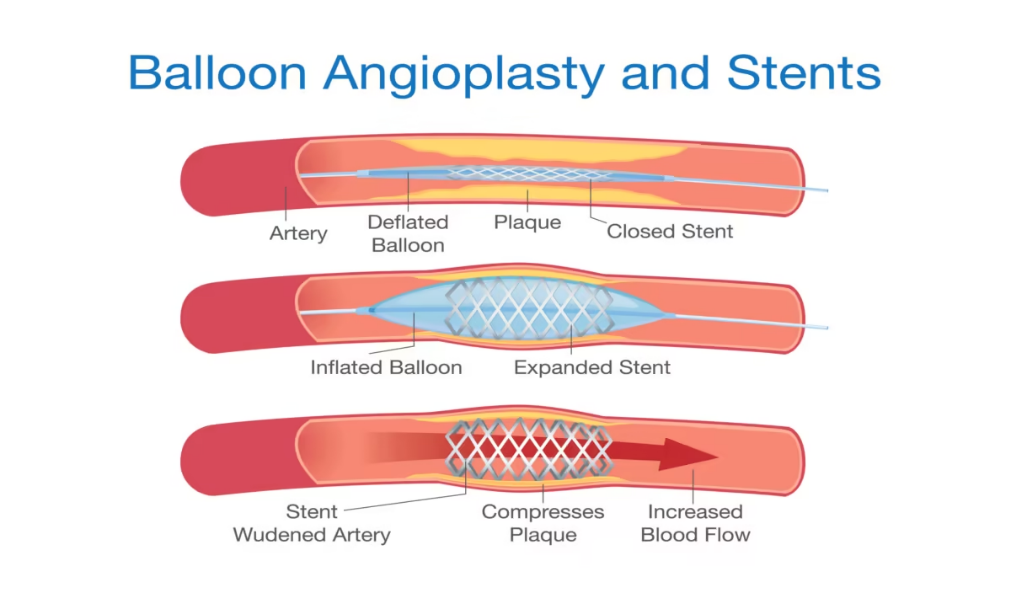
For severe cases or when symptoms worsen despite other treatments, surgery may be needed: Angioplasty and
- Stenting : A balloon widens the artery and a stent keeps it open.
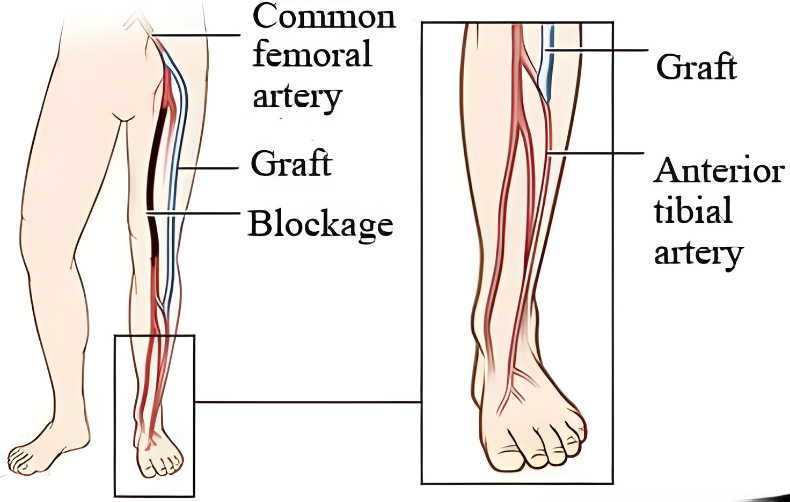
- Bypass Surgery : Redirects blood flow around blocked arteries using a graft.
- Atherectomy : Removes plaque using a catheter with a blade or laser.
In extreme cases, if tissue dies (gangrene), amputation might be necessary but is a last resort. Revascularisation is done prior to amputation in case of dry gangrene (dead tissue without infection). In wet gangrene (dead tissue with super added infection) amputation is done prior to revascularisation to prevent spread of infection into blood (sepsis).
Conclusion
Untreated PAD increases the risk of limb loss. Early diagnosis and treatment improve quality of life and reduce serious complications.
If you experience leg pain or other symptoms, consult our healthcare professionals at “Vizag Surgicare” for proper evaluation and care.
Need Help?
We’re Just a Call Away!
2. Varicose Veins
Introduction
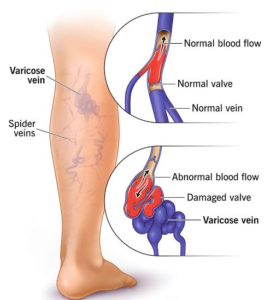
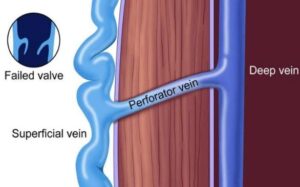
Varicose veins are swollen, twisted (tortuous) veins visible just under the skin, primarily in the legs. They result from weakened vein valves that cause blood to pool, leading to enlarged veins that may cause discomfort and cosmetic concerns.
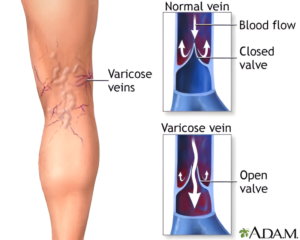
Causes of varicose veins:
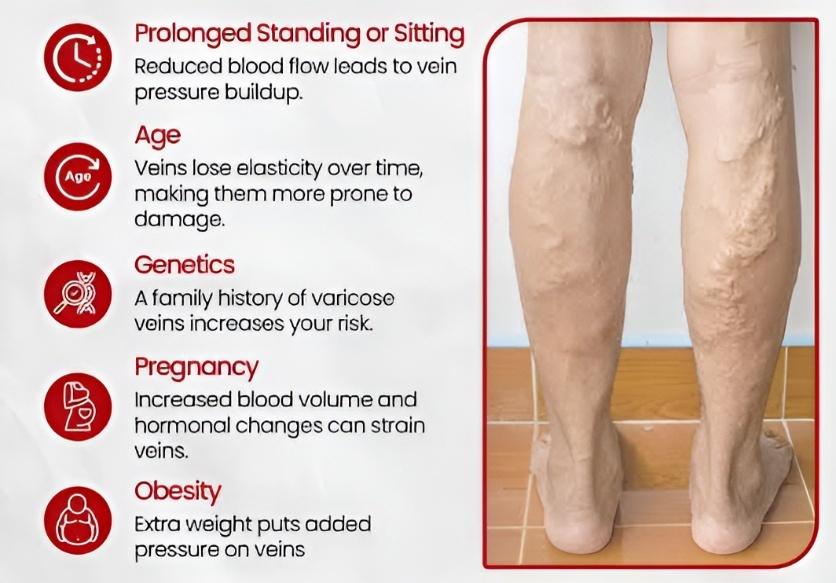
- Standing or sitting for long periods
- Family history of varicose veins
- Pregnancy
- Being overweight
- Aging
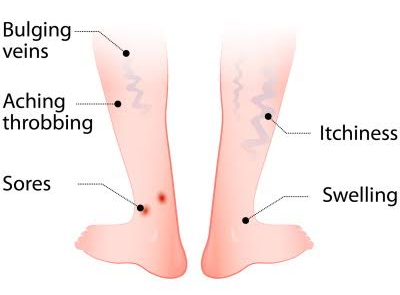
Common Symptoms:
- Bulging, blue or purple veins
- Aching or heavy feeling in your legs
- Swelling in the lower legs or ankles
- Burning, throbbing, or cramping in the legs
- Itchy or dry skin near the veins
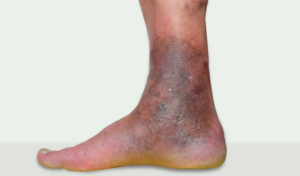
- Sores/ ulcer formation
Symptoms often get worse after standing or sitting for a long time.
Diagnosis:
- Physical examination to look for dilated veins
- Colour Doppler or Duplex scan for confirmation of the disease
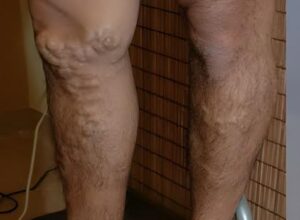
Treatment Options:
Based on symptoms and severity of the condition, treatment is decided – whether to manage conservatively or need any intervention.
1. Lifestyle Changes/ Conservative management
- Exercise regularly to enhance muscle pumping and prevent pooling of blood in legs
- Elevation of legs enhances return of blood
- Wear compression stockings
- Avoid long periods of standing or sitting

2. Minimally Invasive Procedures
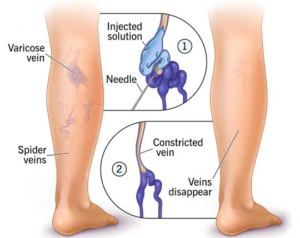
- Sclerotherapy: A special solution is injected into the vein to close the vein.
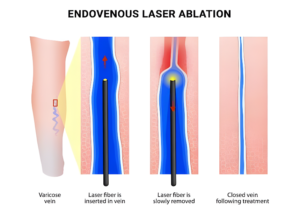
- Endovenous Laser Treatment (EVLT): A small laser fiber is placed inside the vein to seal it by burning the lining and activate fibrosis.
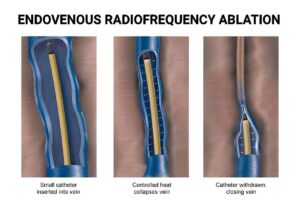
- Radiofrequency Ablation: Heat is used to close the vein
These procedures are done under local anesthesia with no need for hospital stay.
3. Open Surgery
- Ligation and Stripping: All the tributaries (branches of veins which drain at the junction) of Great Saphenous Vein (GSV) are tied and entire vein is removed till below knee joint. It is avoided to remove till ankle joint to prevent injury to nerve.
- Perforator ligation: Tying the perforators (connecting veins between superficial and deep venous system) – this prevents back flow of blood from deep veins into superficial veins.
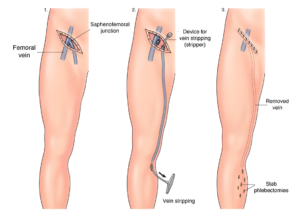
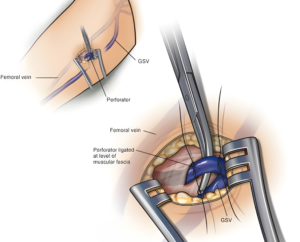
Post procedure care includes wearing compression stockings, engaging in mobility exercises, and adopting lifestyle modifications such as regular walking and leg elevation to enhance recovery and prevent recurrence
Conclusion
If you notice aching on prolonged standing, swelling of limbs, skin ulcers, bleeding, or changes in skin color around varicose veins, seek medical advice promptly. Early treatment can prevent complications and improve symptoms.
If you have symptoms or concerns, consult us at “Vizag Surgicare” for thorough evaluation and personalized care.
contact us
Get In Touch With Us
phone number
Mobile No 1 : +91-77029 50513
Mobile No 2 : +91-9848638615
Mobile No 3 : +91-9849239213
our address
First Floor, Mohan Medical Shop, Seethammadhara (NE), Visakhapatnam-530013
email address
info@vizagsurgicare.com
